线程被称为“最小的处理单元”,是一个轻量级的子进程,分配了一些需要执行的工作。线程共享分配给它们的相同内存插槽,并且彼此独立,因此促进了多任务处理。但是,当多个线程在共享内存插槽上运行时,必然会发生资源竞争。为了避免这种竞争,从而实现高吞吐量,引入了线程优先级的概念。当多个任务在同一个系统上运行时,它具有重要意义。“线程调度器根据优先级分配执行线程”。
JVM(JAVA虚拟机)默认或由程序员明确地决定线程的优先级。优先级在1到10之间,当我们想给线程最高优先级时,就分配10。上下文切换有助于根据优先级顺序从线程1过渡到线程2等等。
注意:可能有两个或更多线程被分配了相同的优先级,那么它们的执行取决于操作系统。例如,Windows使用循环算法来处理这种情况。
Java线程优先级的变量
JAVA中以宏的形式预先保存了三个主要变量,如下所述-
- Public Static int MIN_PRIORITY:这是一个静态变量,带有“
Public”类型的访问修饰符。此变量的值为1。这是为了分配一个优先级最低的线程。 - Public Static int NORM_PRIORITY:这是一个静态变量,带有“
Public”类型的访问修饰符。该变量的值为5。这是为了分配一个具有正常优先级的线程。当开发人员未明确分配优先级时,它是默认优先级。 - Public Static int MAX_PRIORITY:这是一个静态变量,带有“
Public”类型的访问修饰符。该变量的值为10。这是为了分配一个具有最高优先级的线程。
与获取和设置优先级相关的一些功能包括:
Public Final int getPriority():此函数用于获取请求的任何线程的优先级。此函数返回一个整数,因为其返回类型为“int”。整数的范围可以在1到10之间。该功能是公开的和最终的。Public Final void setPriority(int newPriority):此函数用于设置请求的任何线程的优先级。该函数将整数作为参数,函数定义中的参数原型中也提到了这一点。参数整数的范围可以在1到10之间。该功能是公开的和最终的。
Java线程优先级示例
以下是java线程优先级的示例:
下面是一些示例,使用上面已经定义的变量和JAVA中可用的现成函数来演示线程优先级的概念。
代码:
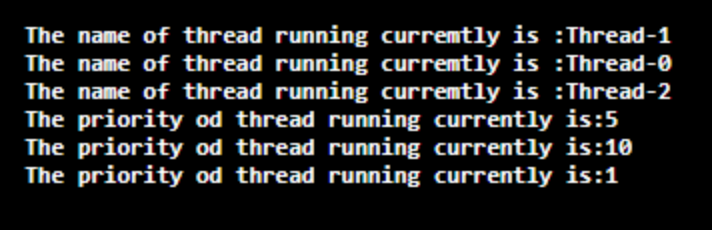
public class test extends Thread{
public void run (){
System.out.println ( "The name of thread running curremtly is :"+Thread.currentThread ().getName ());
System.out.println ( "The priority od thread running currently is:"+Thread.currentThread ().getPriority ());
}
public static void main (String args[]){
test t1=new test ();
test t2=new test ();
test t3=new test ();
t1.setPriority (Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
t2.setPriority (Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
t3.setPriority (Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
t1.start ();
t2.start ();
t3.start ();
}
}输出:
示例2:
下面是一个用户定义的优先级定义和打印示例。
代码:
public class test2 extends Thread
{
public void run ()
{
System.out.println ( " The control is under run function now...");
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
// Here we are creating threads using the constructors.
test2 t1=new test2 ();
test2 t2=new test2 ();
// setpriority () function is used below along with the parameter to set the prioirity.
t1.setPriority (2);
t2.setPriority (9);
// Here we are coding on how to display output strings.
System.out.println ( " The priority assigned to thread t1 is: " + t1.getPriority ());
System.out.println ( "The priority assigned to thread t2 is: " + t2.getPriority ());
// the run () function is defined above will be called via start () function and print the strinf which is there in it.
t1.start ();
}
}输出:

注意:优先级应严格在1到10之间。如果优先级超出此范围,编译器将抛出以下错误。当使用setPriority()函数设置线程t2的优先级时,13被赋予了一个优先级,而不是9。
异常情况:
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.setPriority (Thread.java:1141)
at test2.main (test2.java:14)Java线程优先级的优势
多线程和将优先级分配给以下线程有很多好处:
- 它允许在系统中同时执行多个操作,以及线程的优先级。例如,用户正在网上冲浪,但在安装新软件时突然中断了系统。在这种情况下,优先考虑重新启动系统,而不是上网。
- 如果程序员没有明确定义线程优先级,JAVA线程将从父线程继承其优先级。存在绕过下游线程中的优先级并保持对称性的优先级保留。这使得程序员很容易调试程序。
- 它使代码更简单,因此易于维护。
- 通过分配优先级,它使上下文切换的工作变得更加容易。
结论
这是在同一个系统中操作多个任务的广泛使用且高效的方法之一。由于线程共享内存,因此这种内存有效的方式也是如此。我们可以在系统中运行多个线程,但这可能会混淆处理器,首先选择哪个线程。通过为线程分配优先级,这个问题得以解决。线程继续运行,直到它完成或被优先级更高的线程中断。此功能与操作系统密切配合。
免责声明:本文系转载,版权归原作者所有;旨在传递信息,不代表一休教程网的观点和立场。
