在Java中,Range方法在IntStream和LongStream类中都可用。在IntStream类中,它有助于返回函数参数范围内IntStream的顺序值。在该方法中,startInclusive(inclusive)和endExclusive(exclusive)是与增量步长一起使用的两个参数,如前所述,将包括起始值,并排除结束值。在LongStream的情况下,唯一的区别是添加了LongStream值。
Range语法
让我们看看Java中range方法的语法。
IntStream范围的语法
static IntStream range(int startInclusive, int endExclusive)参数:
- IntStream:这是一个原始类型的int值元素序列。
- startInclusive:包含在范围中的初始值。
- endExclusive:在范围内排除的最后一个值或上限。
返回值:
该方法返回范围中提到的int元素的连续int流作为参数。
LongStream范围的语法
static LongStream range(int startInclusive, int endExclusive)参数:
- LongStream:这是一个基元类型的长值元素序列。
- startInclusive:包含在范围中的初始值。
- endExclusive:在范围内排除的最后一个值或上限。
返回值:
该方法返回范围中提到的长元素的连续长流作为参数。
Range函数在Java中是如何工作的?
首先,让我们看看IntStream范围在Java中是如何工作的。与Java中的其他类类似,这个类也需要一个必须首先导入的包。也就是说,为了使用IntStream类,导入包java.util.stream.IntStream。导入后,创建一个IntStream,以便可以向其中添加元素。创建流后,使用方法range()添加元素。在执行代码时,将通过在参数中提到的范围内的一个增量步骤返回一个序列有序IntStream。
要打印每个元素,请使用如下所示的方法。
intStream.forEach(System.out::println);对于LongStream,首先导入包java.util.stream.LongStream。与IntStream的功能类似,一旦导入包,就创建一个LongStream,以便可以向其中添加元素。创建流后,使用方法range()添加元素。在执行代码时,将通过在参数中提到的范围内的一个增量步骤返回序列有序的长流。
用于使用如下所示的方法打印每个元素。
LongStream.forEach(System.out::println);在for循环的帮助下,可以按顺序生成递增元素的等效打印序列,如下所示。
for (inti = startInclusive; i<endExclusive ; i++)
{... . . . }Java中的Range示例
以下是提到的示例:
示例#1
Java程序实现IntStream Range函数。
代码:
// IntStream range implementation using Java
import java.util.*;
//import the package for IntStream
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class RangeExample {
// main method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an IntStream
IntStream st = IntStream.range(32, 45);
// Display the elements in the range mentioned as 32 and 45 where 32 is included and 45 is excluded
System.out.println("The elements are:");
st.forEach(System.out::println);
} }输出:

首先,导入包java.util.stream.IntStream。然后,创建一个IntStream st,用于向其中添加元素。在创建流的过程中,使用方法range(32,45)添加元素,其中包括32个元素,排除45个元素。在执行代码时,将通过一个增量步骤从32到44返回一个有序的IntStream,如示例输出中所示。
示例#2
Java程序实现LongStream range范围函数。
代码:
// LongStream range implementation using Java
import java.util.*;
//import the package for LongStream
import java.util.stream.LongStream;
public class RangeExample {
// main method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create a LongStream
LongStream st = LongStream.range(1000001L, 1000010L);
// Display the elements in the range mentioned as 1000001L and 1000010L where 1000001L is included and 1000010L is excluded
System.out.println("The elements are:");
st.forEach(System.out::println);
} }输出:
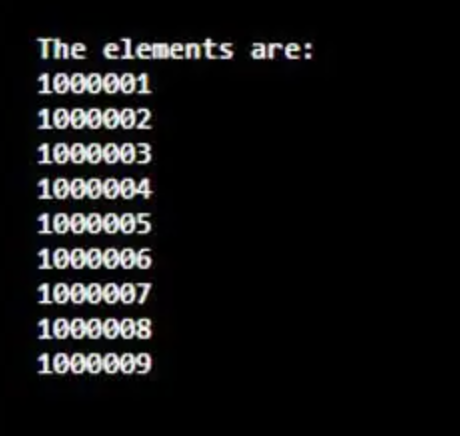
与上述程序类似,导入包java.util.stream.LongStream。然后,创建一个具有方法range(100001L、100010L)的LongStreamst,用于向其添加元素。在执行代码时,将通过一个增量步骤从100001L返回到100010L,如示例输出所示。
示例#3
Java程序,用于组合实现LongStream和IntStream range范围函数。
代码:
import java.util.*;
//import the package for IntStream
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
//import the package for LongStream
import java.util.stream.LongStream;
public class RangeExample {
// main method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an IntStream
IntStream str = IntStream.range(32, 45);
// Display the elements in the range mentioned as 32 and 45 where 32 is included and 45 is excluded
System.out.println("The IntStream elements are:");
str.forEach(System.out::println);
// Create a LongStream
LongStream st = LongStream.range(1000001L, 1000010L);
// Display the elements in the range mentioned as 1000001L and 1000010L where 1000001L is included and 1000010L is excluded
System.out.println("The LongStream elements are:");
st.forEach(System.out::println);
} }输出:
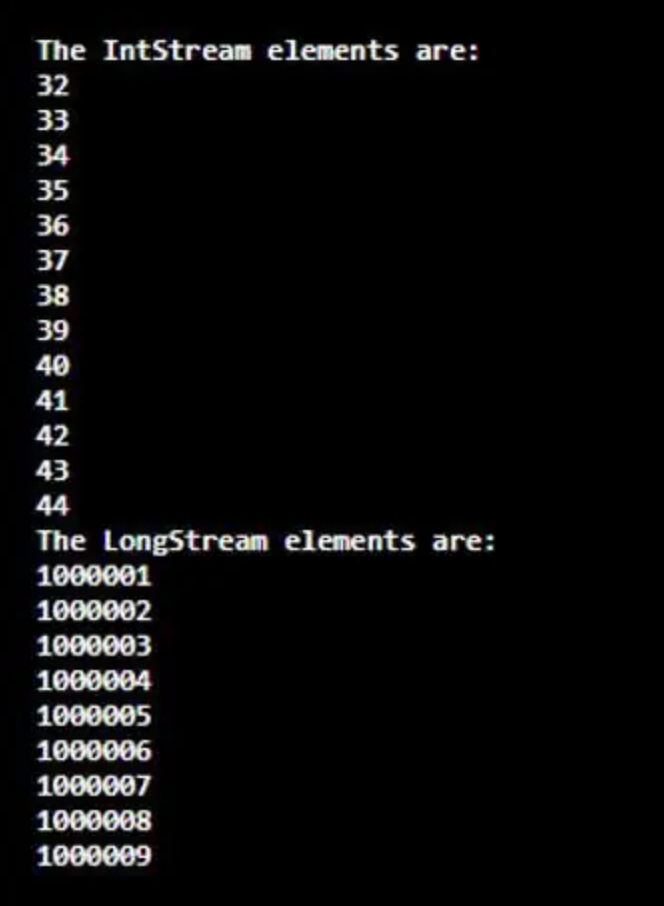
导入包java.util.stream.IntStream 和 java.util.stream.LongStream。然后,创建IntStreamstr和LongStreamst以向其中添加元素。在创建流期间,使用方法range(32,45)在IntStream中添加元素,其中包括32,排除45。同样,使用方法range(100001L、100010L)在LongStream中添加元素。在执行代码时,序列有序IntStream将从32返回到44,LongStream将通过增量步骤1从100001L返回到100010L。
结论
Java中的range方法用于返回IntStream和LongStream在函数参数范围内的顺序值。
